Huygen’s Principle
Huygen’s Principle: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Wave Optics, Phase of Waves, Spherical Wavefront, Plane Wavefront, Cylindrical Wavefront, Secondary Wavelets, Speed of Light Waves, Huygens Wave Principle, Sources of Light Waves and, Types of Wave Fronts
Important Questions on Huygen’s Principle
The surface of sphere with source as center and distance travelled by light wave as radius where each wave arrives simultaneously is called _____ .
A Wavefront is defined as the locus of points that are in the same phase.
A plane wavefront passing through a concave lens converges to a point.
Assertion: When a plane wave passes through a thin prism, the emerging wavefront gets titled.
Reason: Speed of light is less in glass than in air.
Ray is the locus of points in the light wave’ having the same phase of oscillation at any instant.
Two sources of monochromatic light are said to be coherent, if light waves produced by them have the same
The shape of the wave front originating from a line is spherical.
Illustrate with the help of suitable diagram, action of the following when a plane wavefront incidents on a prism.
A plane wave front falls on a convex lens. The emergent wave front is spherical _____.
A plane wave front falls on a convex lens. The emergent wave front is spherical converging.
Draw a diagram to show the refraction of a plane wave front incident on a convex lens and hence draw the refracted wavefront.
The Huygen's wave theory is failed to explain the photoelectric effect because:
The phenomenon of light that can be explained using Huygen's theory of light is/are:
A monochromatic plane wave of speed c and wavelength is diffracted at a small aperture. The diagram illustrates successive wavefronts (vibrating in the same phase). After what time will some portion of the wavefront reach ?
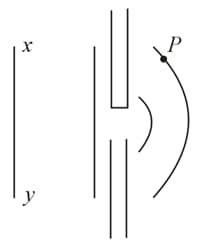
Spherical wavefronts shown in figure, strike a plane mirror. Reflected wavefronts will be as shown in
Light waves travel in vacuum along the -axis. Which of the following may represent the wavefront?
